The flora encountered in Analamerana includes typical elements of the dry dense forest and locally endemic species in the north. From a faunal point of view, due to its climate and the relatively bare character of a good part of its surface, the reserve does not promote the abundance of reptiles or amphibians. However, the site harbors an important population of Propithecus perrieri, which is a lemur species restricted to the extreme north of the island and is considered critically endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. …
Archives: Aires protégées
Analamazaotra
The park mainly houses a mid-altitude dense humid forest. Despite its small size, it has a high biological diversity for both fauna and flora. …
Ambohitantely
The Ambohitantely Special Reserve ensures the representation of the central terrestrial ecoregion. The Reserve is home to a palm species, the Dypsis oropedionis, which requires particular attention given its status within the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the pressures weighing on it. This palm is also among the conservation targets of the Protected Area (PA). …
Andranomena
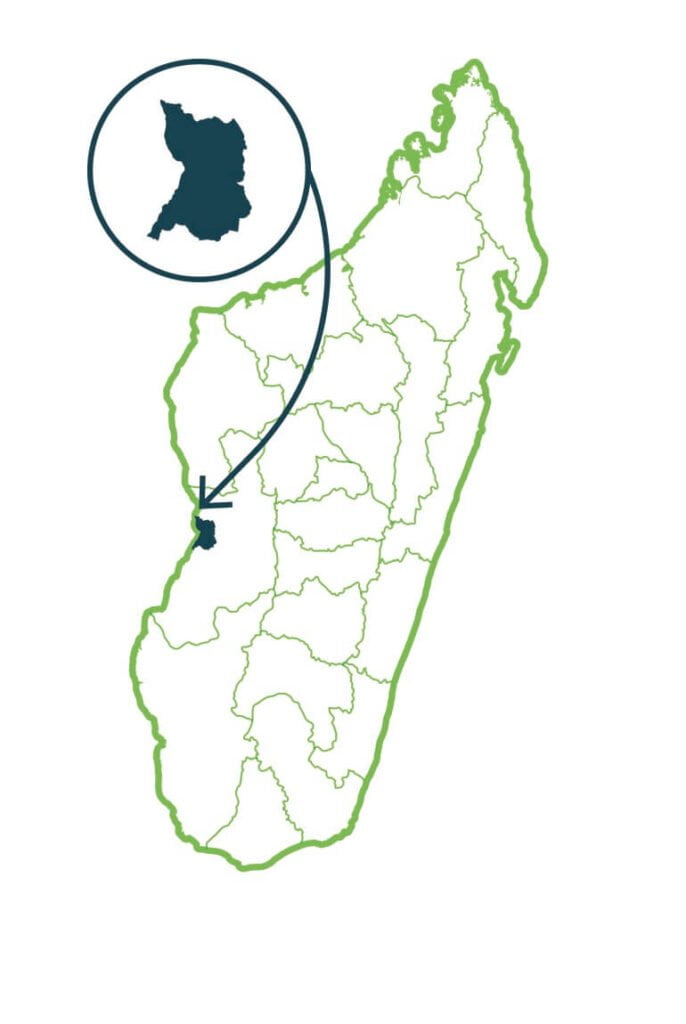
The northern part of the Special Reserve of Andranomena shelters a relatively dense dry forest while the central and southern parts present slightly degraded forms. In favor of some basins, there are also small lakes, mainly temporary, surrounded by grassy swamps. The southern and eastern limits are covered with secondary formations where some sacred baobabs remain. Among the flagship species, Andranomena is home to the flat-tailed turtle and the smallest primate in the world, the microcèbe of Mme Berthe. …
Lokobe
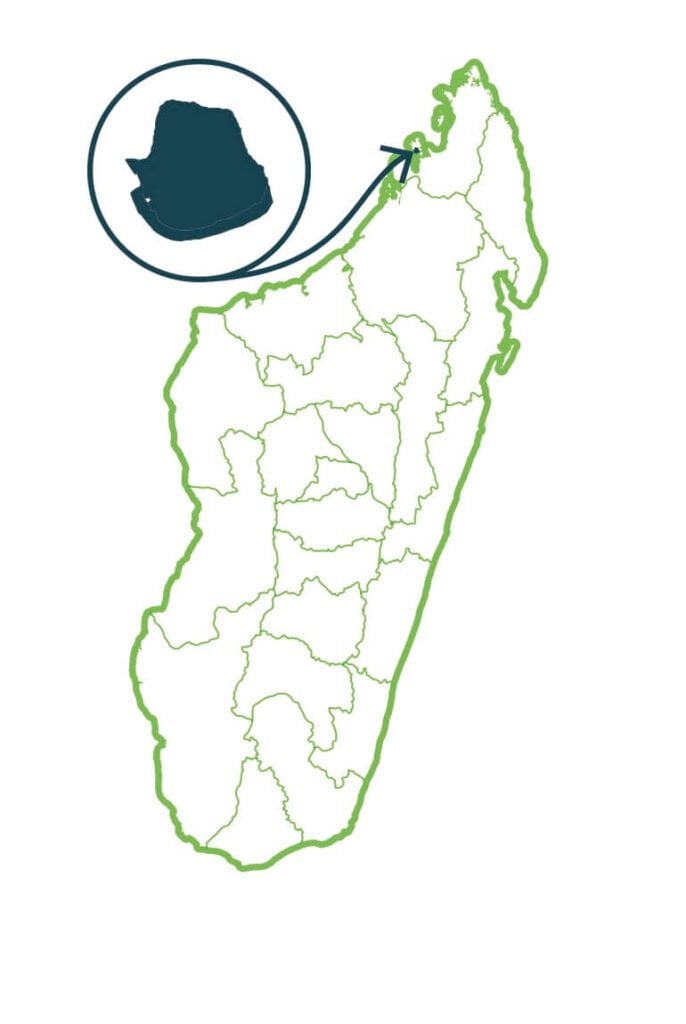
The Lokobe forest represents one of the last remnants of lowland dense evergreen forest in the Sambirano phytogeographic domain. Two main ecosystems are found in the park: the terrestrial ecosystem and the marine ecosystem. The terrestrial parcel of Lokobe shelters remarkable species like lemurs with very restricted distribution, and threatened species of palms such as Dypsis ampasindavae. The marine parcel located south of the terrestrial parcel is made up of coral reef and phanerogam meadows as well as a very small area of mangrove. …
Manongarivo
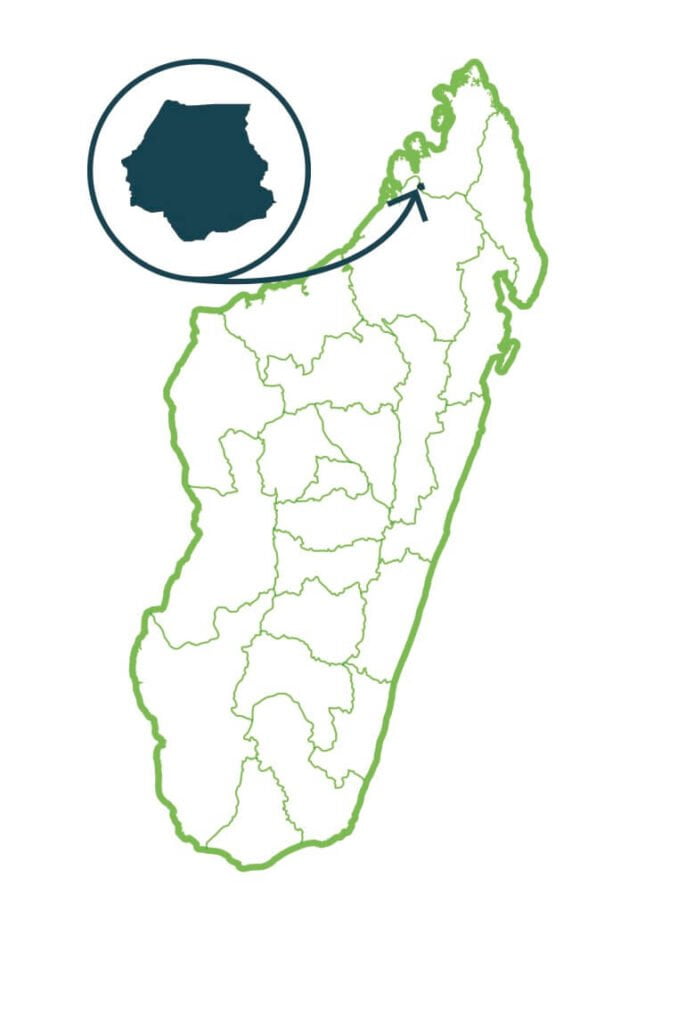
National Park of Lokobe and the Special Reserve of Manongarivo are the last representatives of the dense forest of the phytogeographic domain of Sambirano. With the different vegetal formations that are found there, the reserve registers an exceptionally rich biological diversity as much from the floristic point of view as faunistic. From a floristic point of view, it’s to should be noted that the vegetation of the reserve is essentially forest with several species restricted to the dense humid forests of the North. For the fauna, it shelters lemurs reminding its belonging to the domain of Sambirano, notably the Avahi and the microcèbe of Sambirano. It is also home to two species of chameleons of the genus Brookesia locally endemic. …
Nosy Mangabe
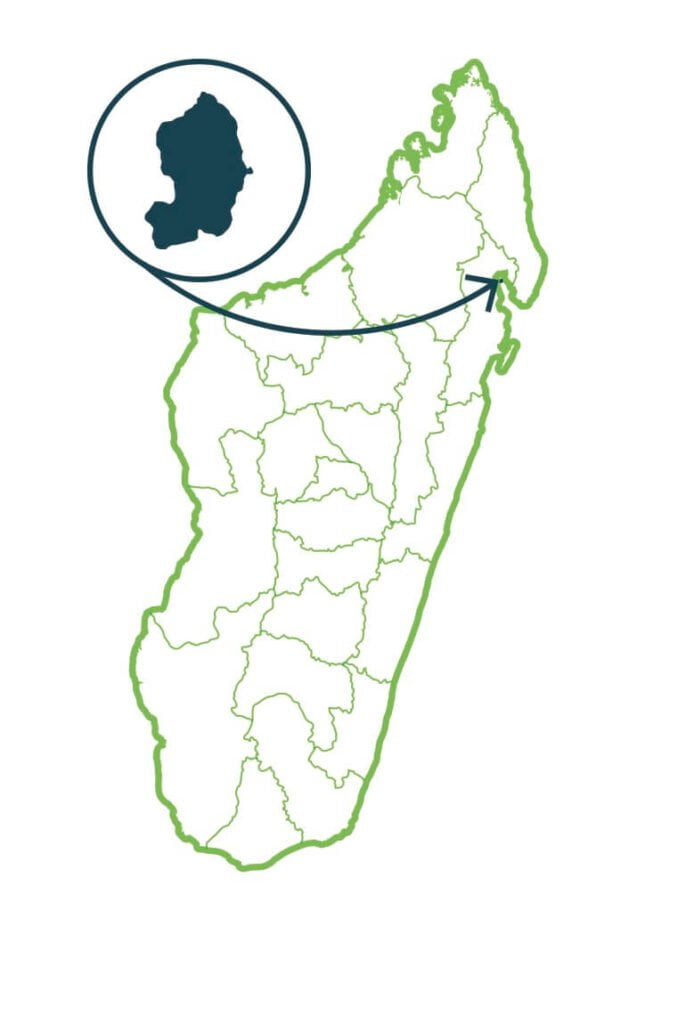
The park is formed by four islets: Nosy Mangabe, Nosy Milomboko, Nosy Haramy and Nosy Ravina. The islet Nosy Mangabe is totally covered with natural forests from the sea level to its highest peak. In terms of biodiversity, we can say that Nosy Mangabe, despite its relatively small size, is quite rich. The insularity implies a relatively reduced animal diversity in comparison with other forests of the same type on the mainland. However, reptiles are particularly abundant, probably due to the low level of disturbance and the scarcity and absence of certain species of raptor birds and carnivorous mammals. The park also supports local endemic species of amphibians: “Rhombophryne mangabensis” and “Stumpffia dolchi”. …
Namoroka
The National Park of Namoroka is constituted by a massif of lapiezed limestones or “Tsingy” essentially forested in its northern half, and by a landscape of meadows and secondary pastures in the southern half. The floristic species that are met there are known to have morphological characteristics of particular adaptation. From the fauna point of view, the park shelters an important fauna of bats, with the highest specific diversity among all the protected areas, thanks to the presence of numerous caves. …
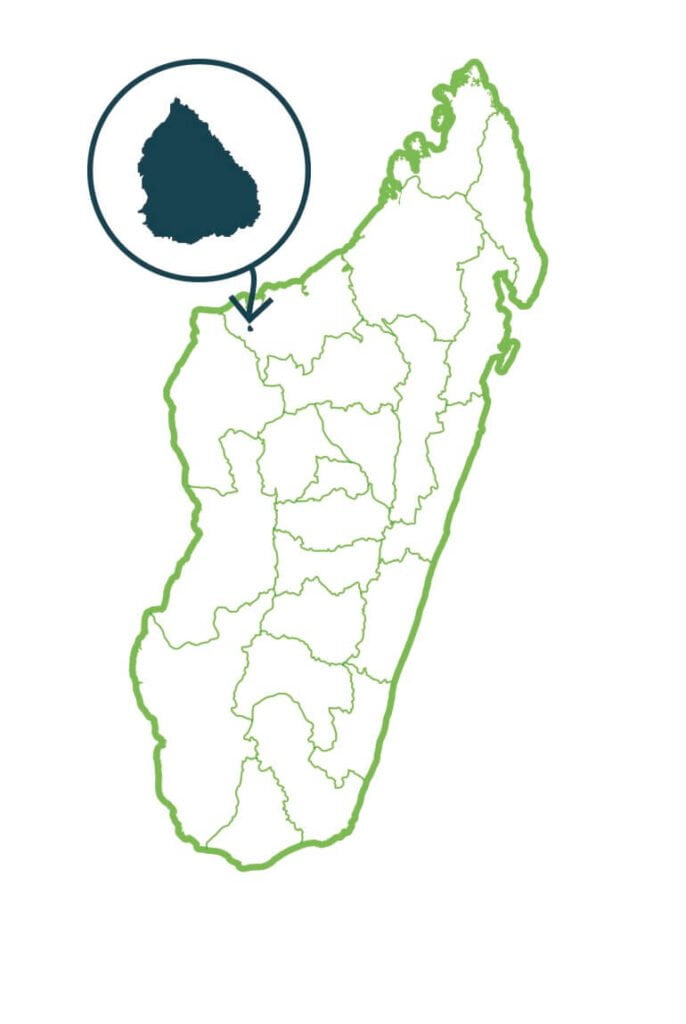
Ivohibe
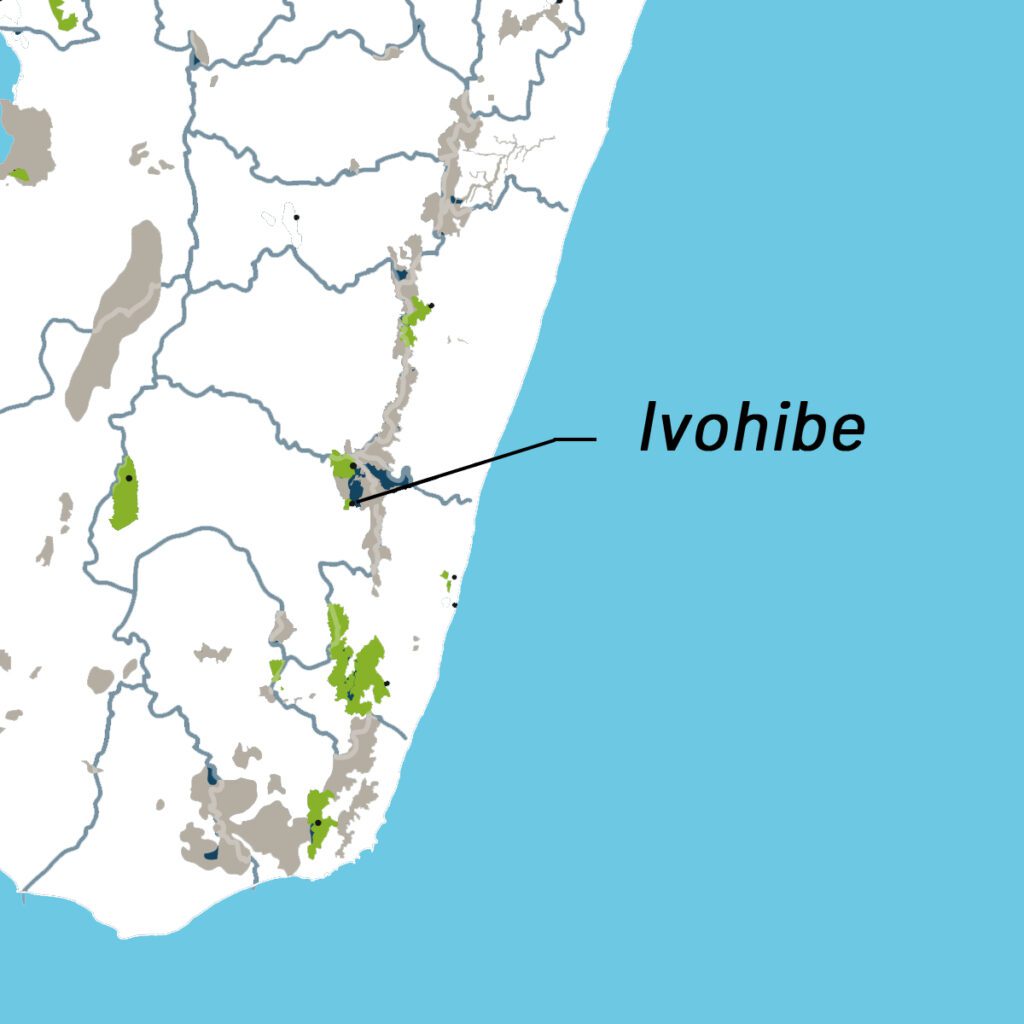
The Ivohibe massif is a southern part of the Andringitra chain. The Reserve belongs to the ecoregion of the center and the ecoregion of the east. It is representative of the humid dense forests of low and medium altitude. The flora that we find there includes typical elements of the dense humid evergreen forest, as well as species restricted to the high plateaus of the Southeast and local endemics. As for the fauna, the reserve shelters a great biological richness even if no locally endemic species have been recorded there: 8 species of lemurs whose distribution is relatively restricted to the South-East (e.g.: Propithecus edwardsi, Avahi peyrierasi). …
Ambodivahibe
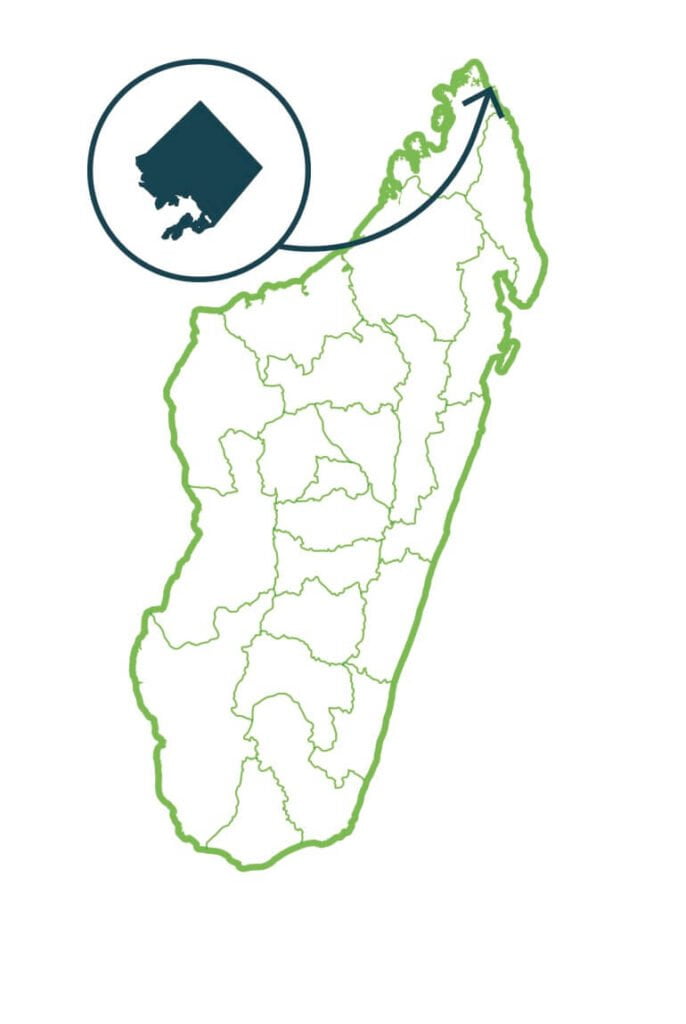
Ambodivahibe is a narrow and steep continental shelf,resulting in deep and narrow bays with canyons leading to deep water, where strong upwelling is observed. This site covers the continental shelf from the shoreline to the shelf edge, encompassing many types of bays and islands. The NAP is characterized by habitats specific to the marine and coastal ecoregion: coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass areas, beach, rocky shores and islets. They are nesting sites, feeding areas, development areas and dormitories of several species including sea turtles, terns, bats, crustaceans, reef fish, mollusks and echinoderms. Most of the fauna found there are species adapted to high salinity. …
Ibity
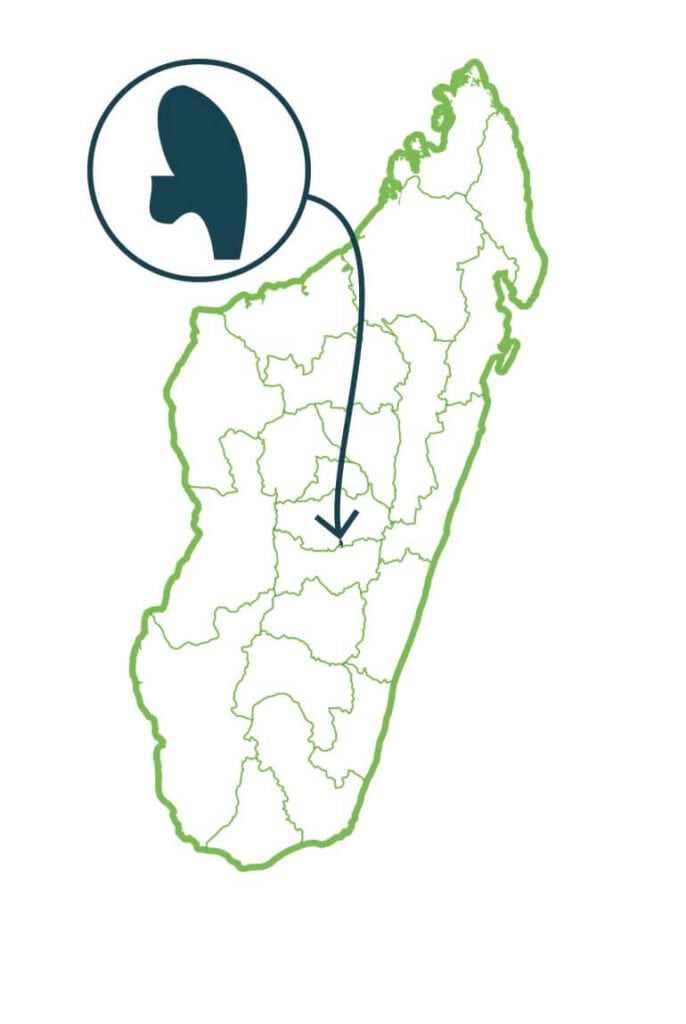
The New Protected Area (NPA) is essentially a large mountain populated by herbaceous dominated vegetation (four main types), largely shaped by the actions of fires. The woody vegetation occupies only very small areas. The great importance of the quartzite’s outcropping is conducive to the rocky vegetation where we observe an important procession of local endemic species. The massif also shelters a not negligible surface of forest of tapia. …
Andrafiamena Andavakoera
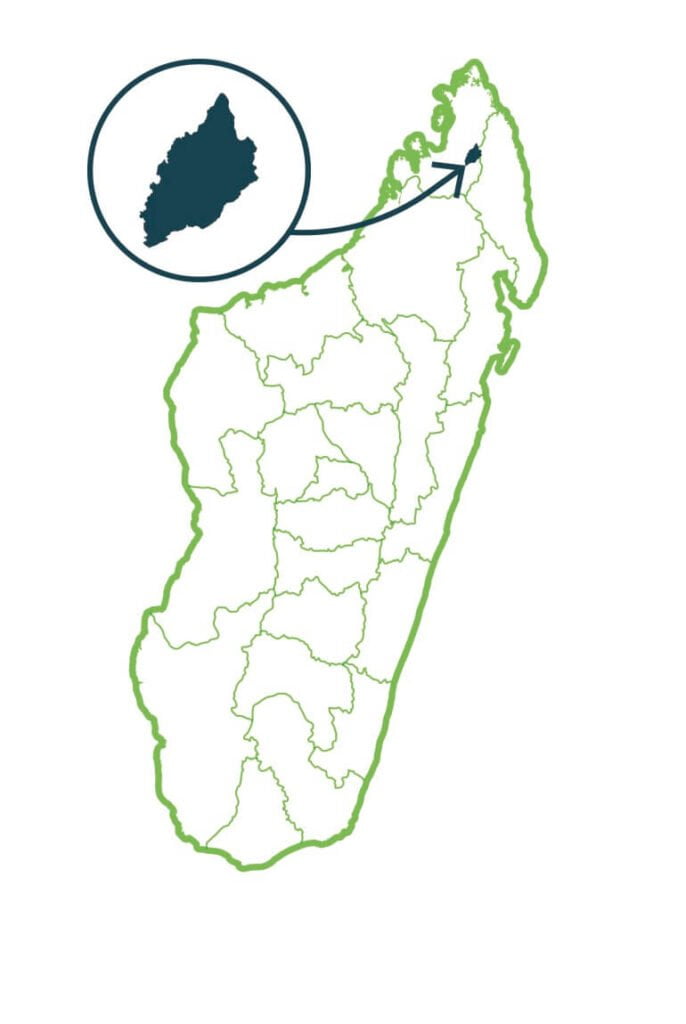
The Andrafiamena-Andavakoera complex is one of the rare areas in the north of Madagascar where one meets various types of plant formation at the same time going from subhumid forests along the slopes on sandstone soil, to dry forests on karst, the “Tsingy”. This diversity of habitat also leads to a great wealth of biodiversity. The natural forests of the Andrafiamena range constitute the exclusive habitat of the lemur species: Propithecus perrieri. …
Ankivonjy
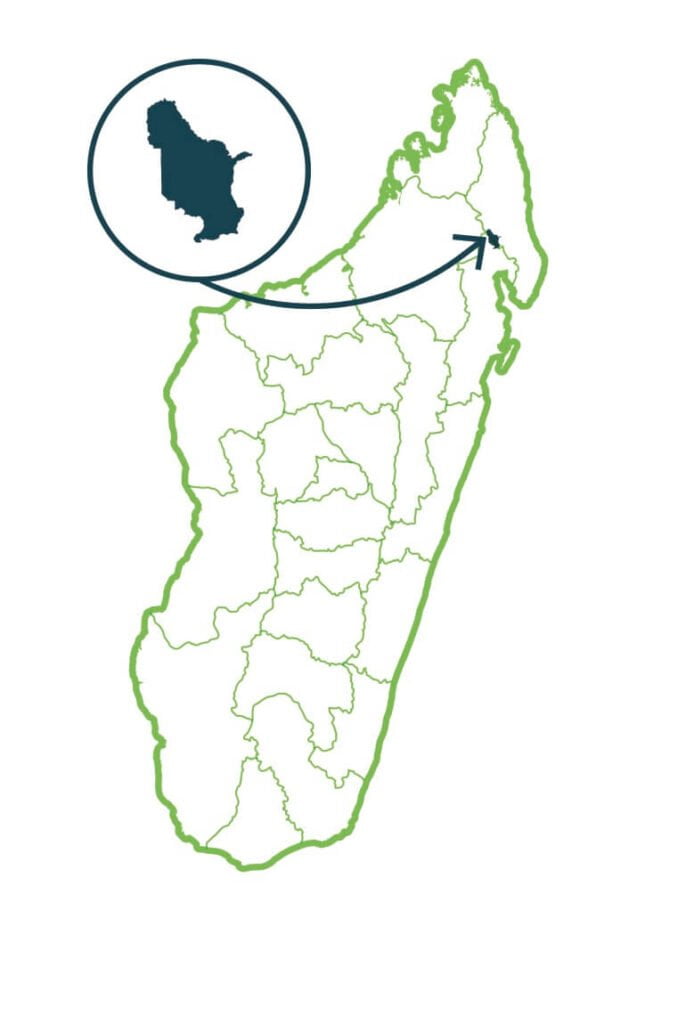
Ankivonjy has a strong landscape value. It specifically shelters the island of Nosy Iranja with its two islets Iranja Kely and Iranja Be connected by a white sand bank uncovered at low tide, the island of Ankazoberavina with its dense vegetation identical to that of the rainforest of the East, Nosimborona Island, Nosy Ankisomany the Sugar Loaf Ankivonjy, and the bay of the Russians surrounded by mangrove forest. It is also distinguished by its richness in biodiversity belonging mainly to the marine domain. …
Menabe Antimena
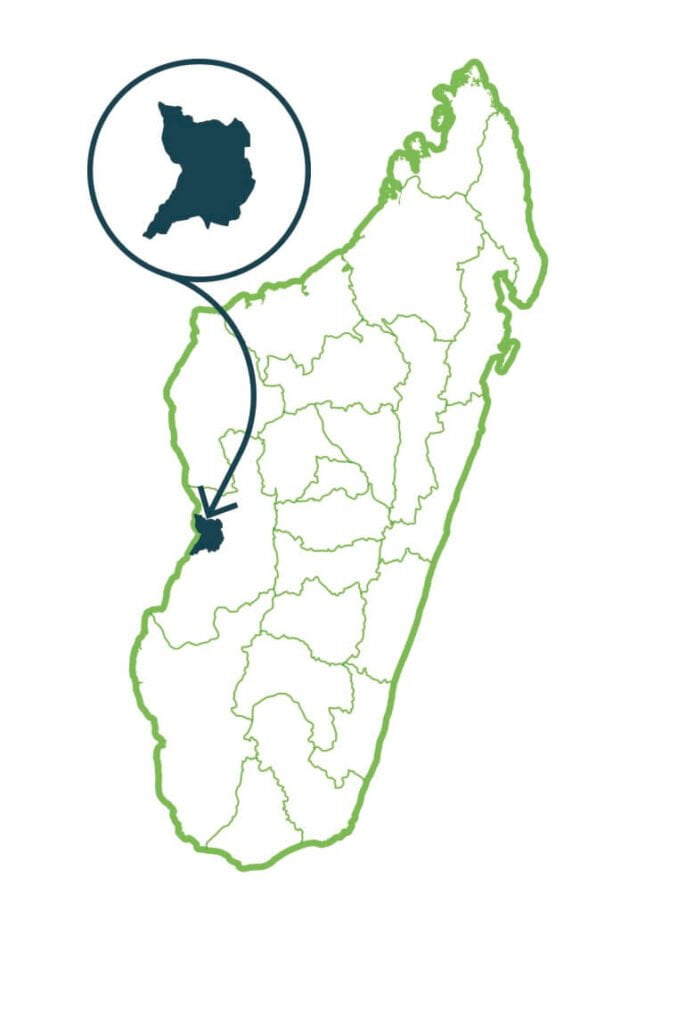
Menabe Antimena is constituted by an exceptional biological diversity. It is characterized by large contiguous blocks of natural habitats such as dense dry forests, Lake Kimanaomby, Lake Bedo and mangroves with a center of micro endemism. The dense dry forests are home to many endemic species such as Hazomalany, rosewood and baobabs. They also constitute the main habitat of the flagship species of the Menabe Antimena including the giant jumping rat, the flat-tailed turtle, the smallest primate in the world (Madame Berthe’s mouse lemur), the mongoose with fine stripes and the fosa. The lakes are home to many species of birds. …
Anjanaharibe Sud
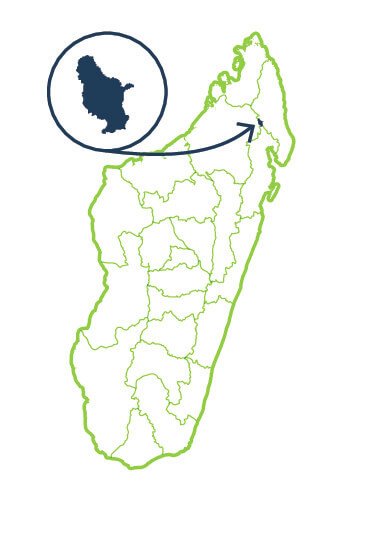
The Anjanaharibe-Sud massif occupies the southwestern part of the Andapa basin watershed. Anjanaharibe-Sud has a rich vertebrate fauna, including many endemic species with restricted geographical distribution. One of these is the silky sifaka, which is one of the world’s rarest and most critically endangered primates. The park is also the northernmost refuge for the Indri indri. The majority of the natural habitat in Anjanaharibe-Sud is composed of dense evergreen mid-altitude rainforest. …
Ankarana
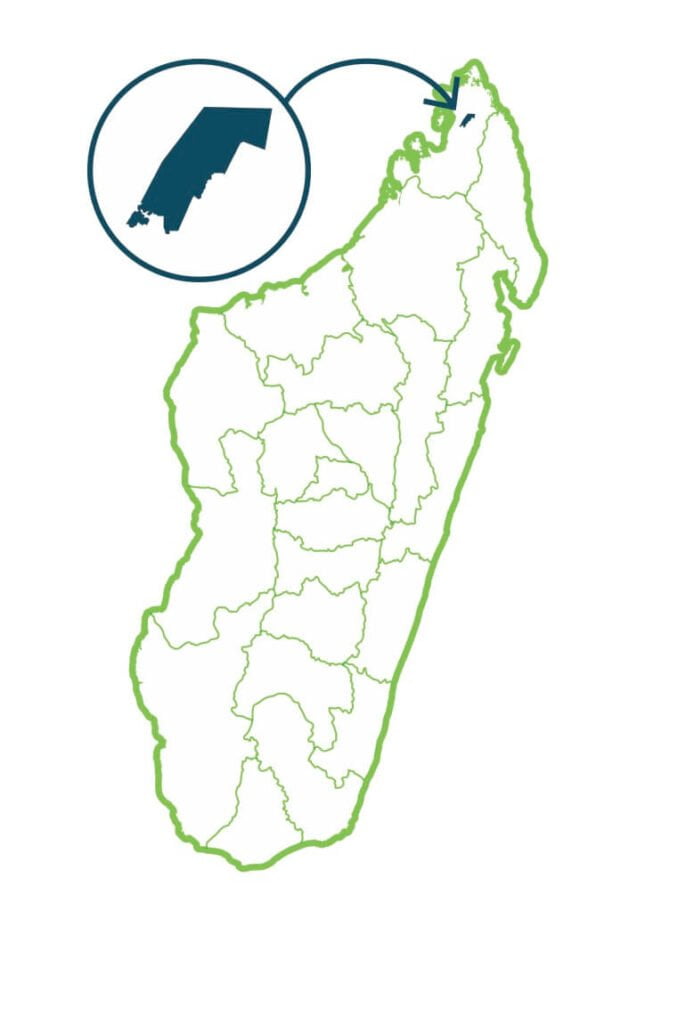
The Ankarana Special Reserve was created in 1956. It is home to ecosystems complex made up of dry decidious forests, Tsingy, dry and wet caves, canyons, underground networks, savannas, sinkholes and lakes. The Ankarana Special Reserve is rich in biodiversity, among which the most characteristic are xerophytic plants on limestone rocks (Euphorbia ankarensis, Tacca ankarensis), cave species (17 bats species including Eidolon dupreanum), aquatic species (Glossogobius ankarensis) and lemurs (Lepilemur ankaranensis and Microcebus tavaratra). …
Complexe Tsimembo Manambolomaty
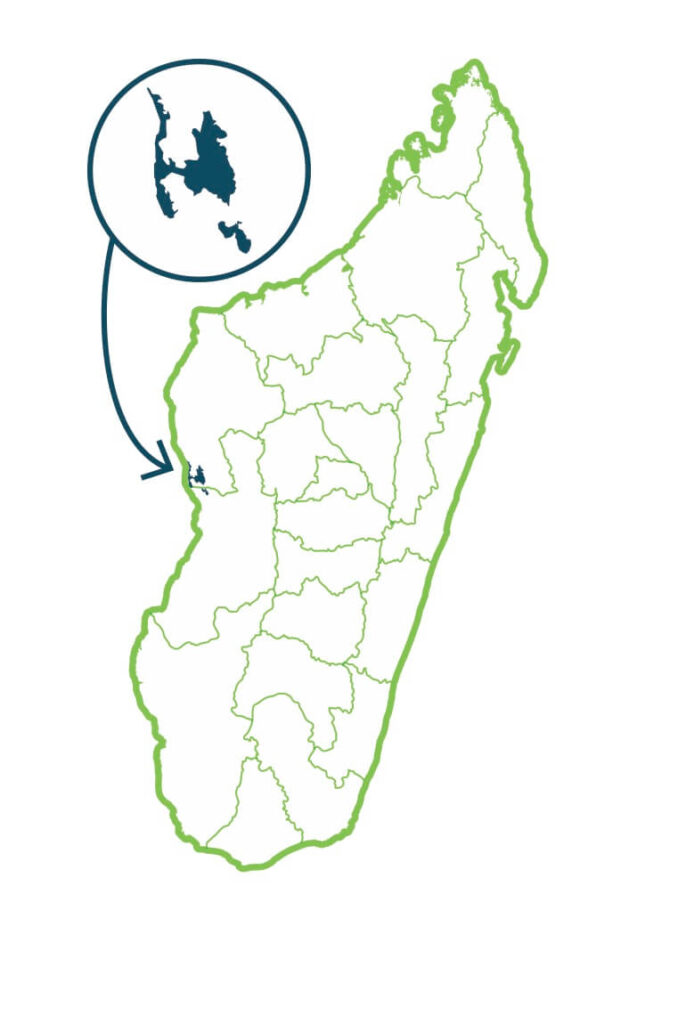
3 types of natural habitats coexist in this protected area: dry deciduous forest, mangroves and lakes. The lake ecosystem offers fishermen significant and stable sources of income through the rational management of the protected area. The products of these fishing activities can supply Morondava and even Antananarivo markets. Propithecus deckenii and Haliaeetus vociferoides (the Madagascar eagle) are among the iconic fauna in this protected area. …
Oronjia
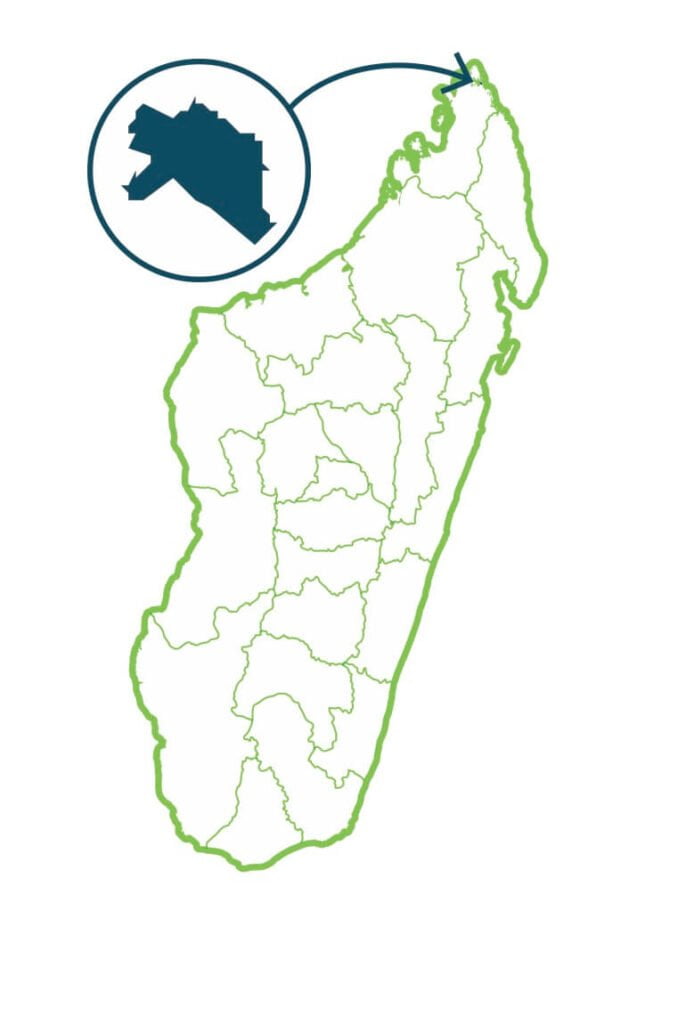
The vegetation of the protected area is characterized by a degraded dry plant formation on sand and limestone. There are 290 species of plants, 70% of which are endemic to Madagascar and some endemic species of the region including Dioscorea orangeana, which is heavily exploited by the local populations for their food during the lean season. The fauna is composed of 2 species of lemurs, 37 species of reptiles, 5 species of amphibians and 77 species of birds. This area of Northern Madagascar is recognized for its importance for the conservation of avifauna and herpetofauna. …
Montagne des Français

The main ecological values of the NPA Montagne des Français concern both its natural habitats and the flagship species it hosts. There are several types of plant cover including semi-deciduous dense dry forest, sub-humid forest or gallery forest, and typical Tsingy vegetation. The fauna and flora are characterized by forms endemic to this northern region of Madagascar. …
Maromizaha
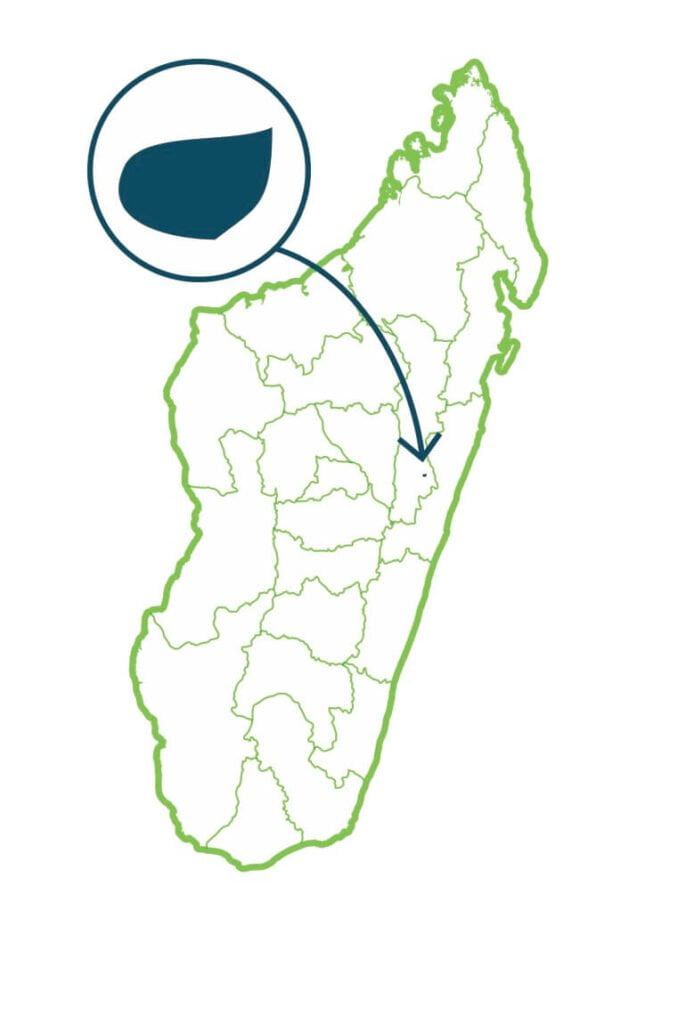
The climax of Maromizaha is the dense rainforest type. The protected area shelters 3 types of natural habitats: the primary forest, the secondary forest and the savoka or forest in regeneration after the slash-and-burn practice. The vegetation belongs to different phytogeographic types: wind flora, the eastern eco-floristic zone of low and medium altitude, and the rainforest. There are 13 plant families with 26 species, 88% of which are endemic to Madagascar. Lemurs are represented by 12 species including Indri indri and Propithecus diadema. …




