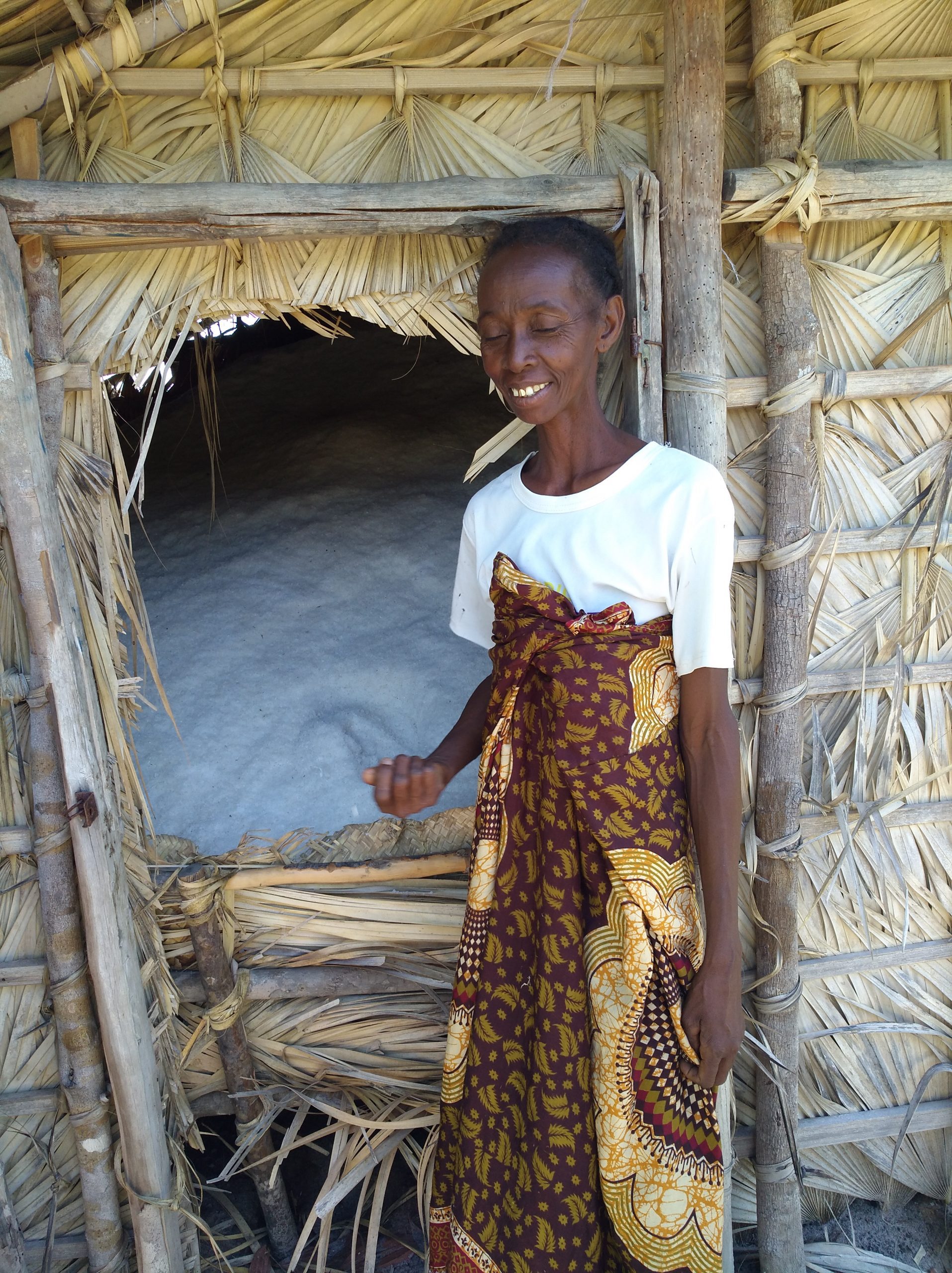
Flagship Species
It was a multiple-use forestry station in 2000, this biocultural site obtained its final protection status in 2015. This protected area covers a 1,000 hectare marine park, dry forests on dune and lateritic soils, several freshwater lakes and mangroves.
Dry forests on dune are only found in the deciduous dry forest ecoregion south of Morombe.
The Propithecus coronatus is the flagship species of this biocultural site.