Flagship Species
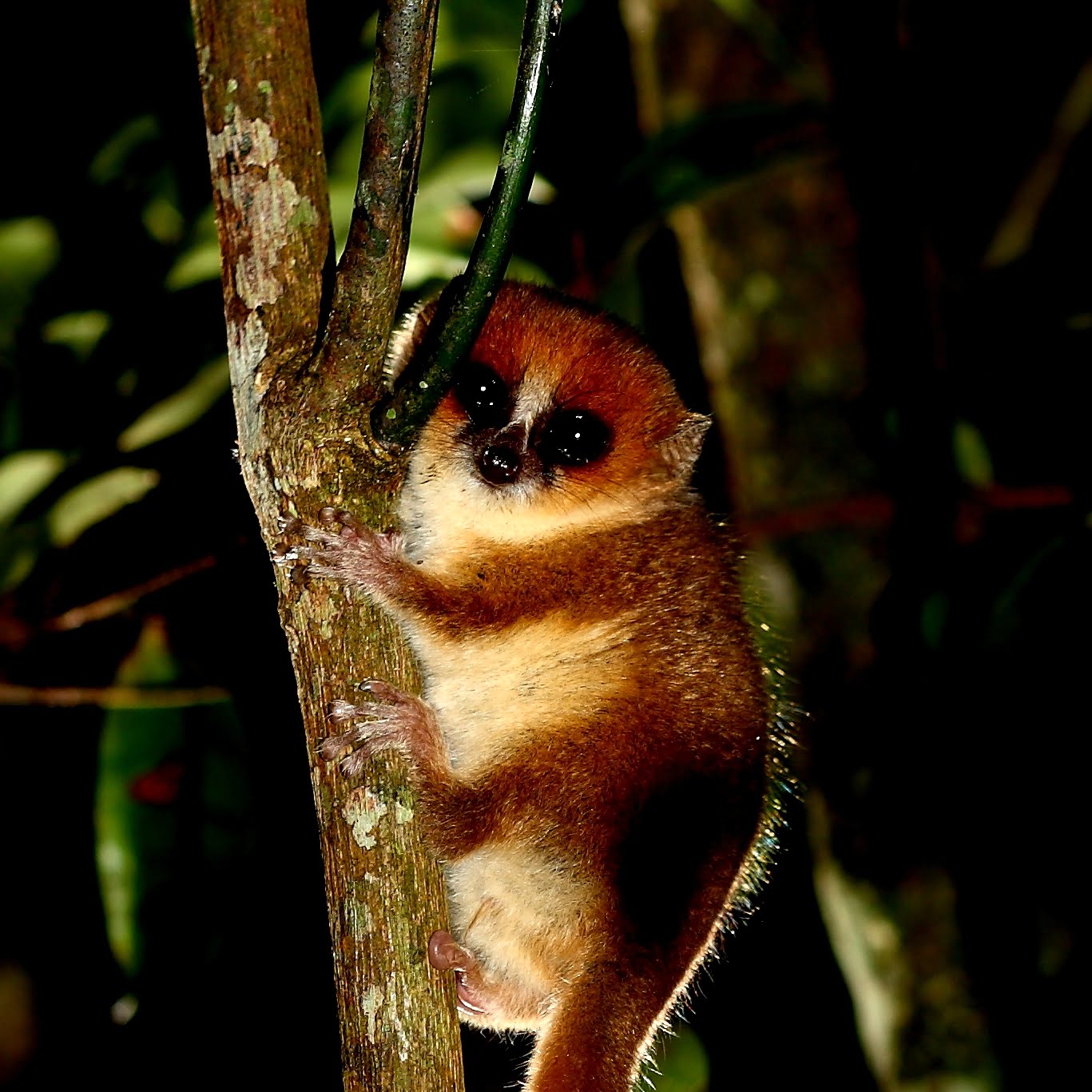
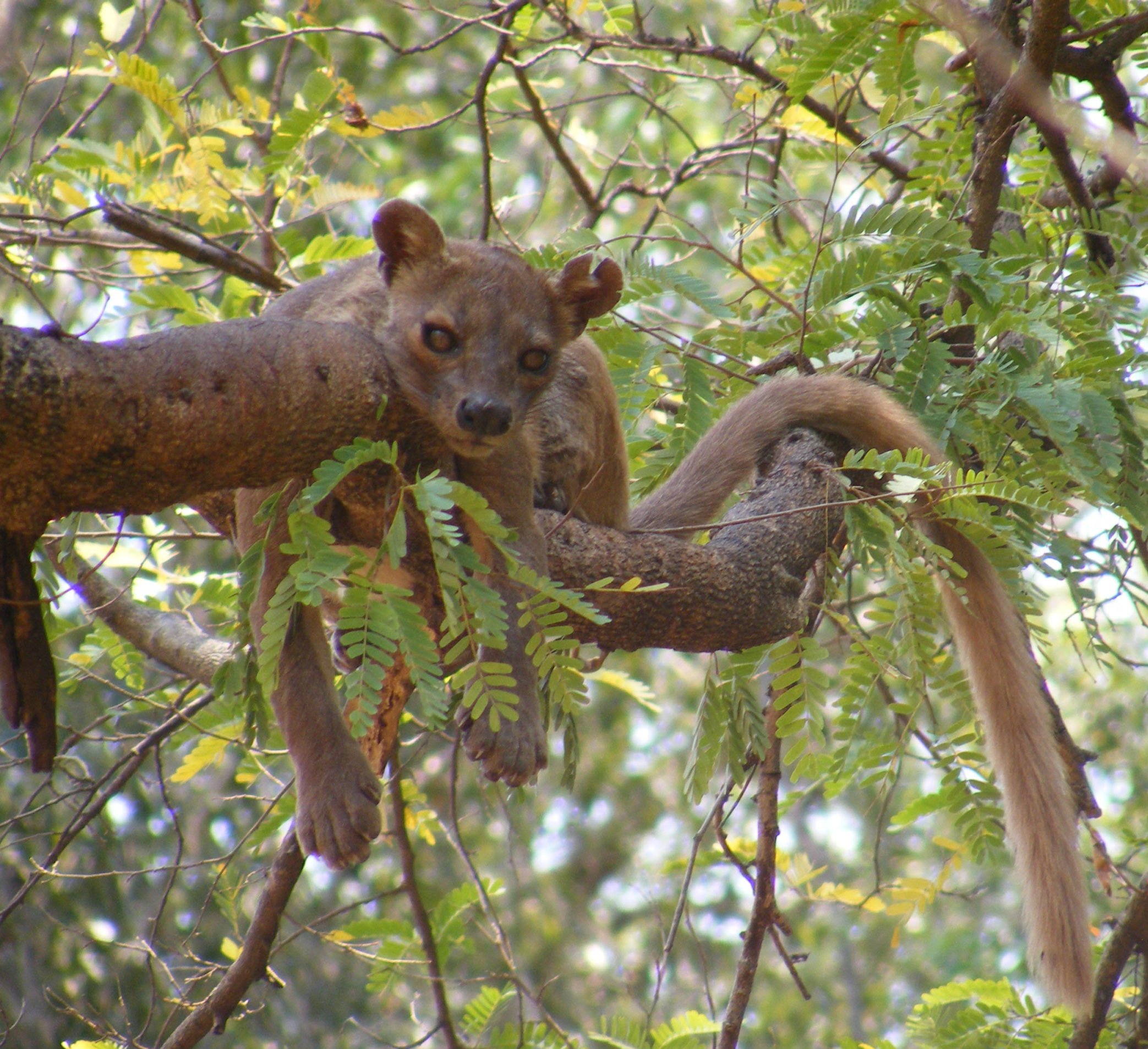
Vegetation consists mainly of lowland moist evergreen forests. There are 7 species of lemurs, including the Eulemur cinereiceps, which is endemic to this region, up to the Agnalazaha Reserve.
72 birds species have been listed, the most emblematic of which are the Leptosomus discolor and the Madagascar Rail (Rallus madagascariensis). Manombo Reserve is also known for its richness in snail species. There are 52 species of snails, most of which are endemic.