Flagship Species
The Baly Bay National Park is of critical importance for the in situ conservation of the critically endangered Angonoka turtle (Astrochelys yniphora).
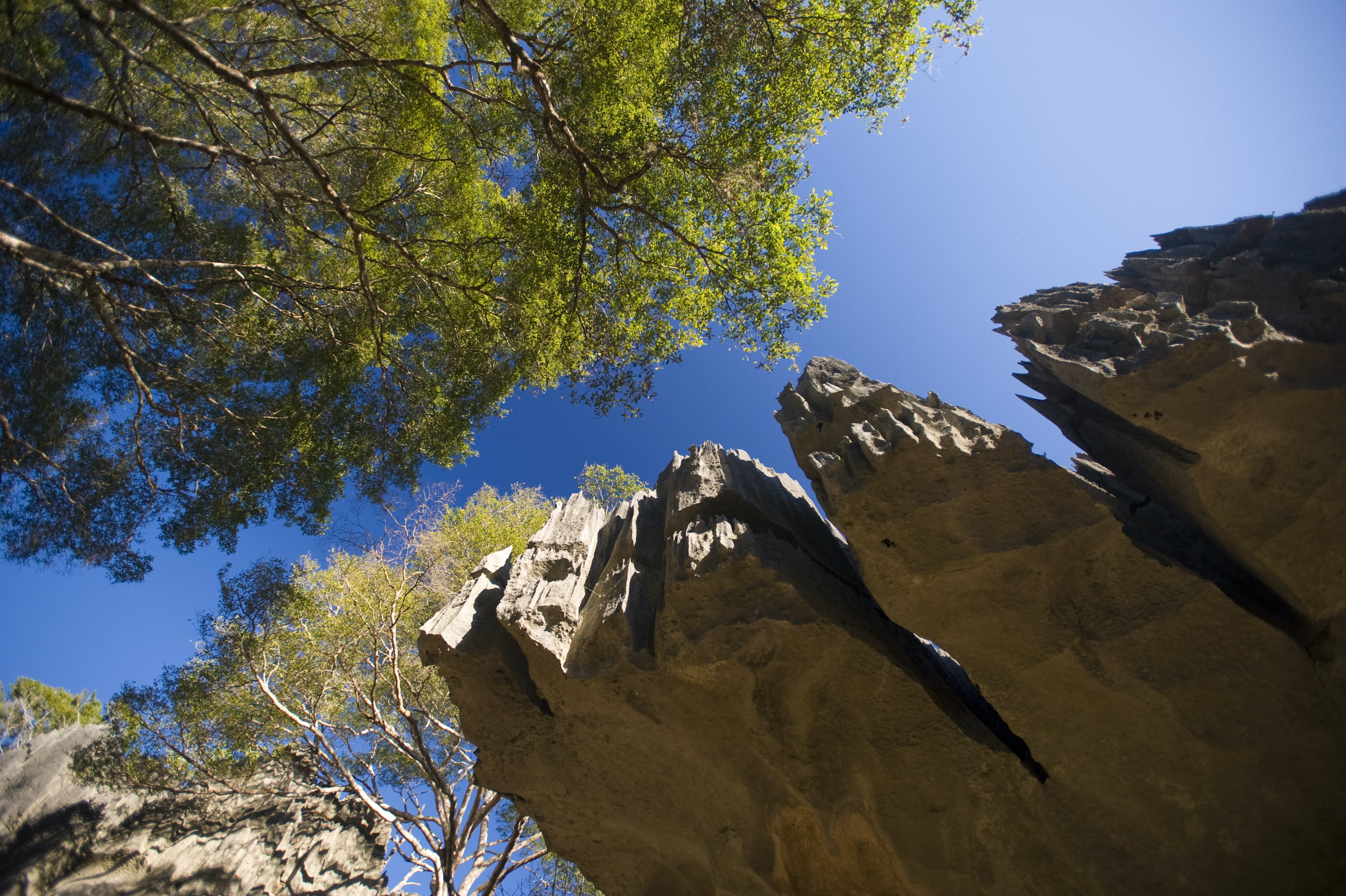
The vegetation is composed of dense dry semi-caducifolia forests, Tsingy, mangroves and wooded savannah.
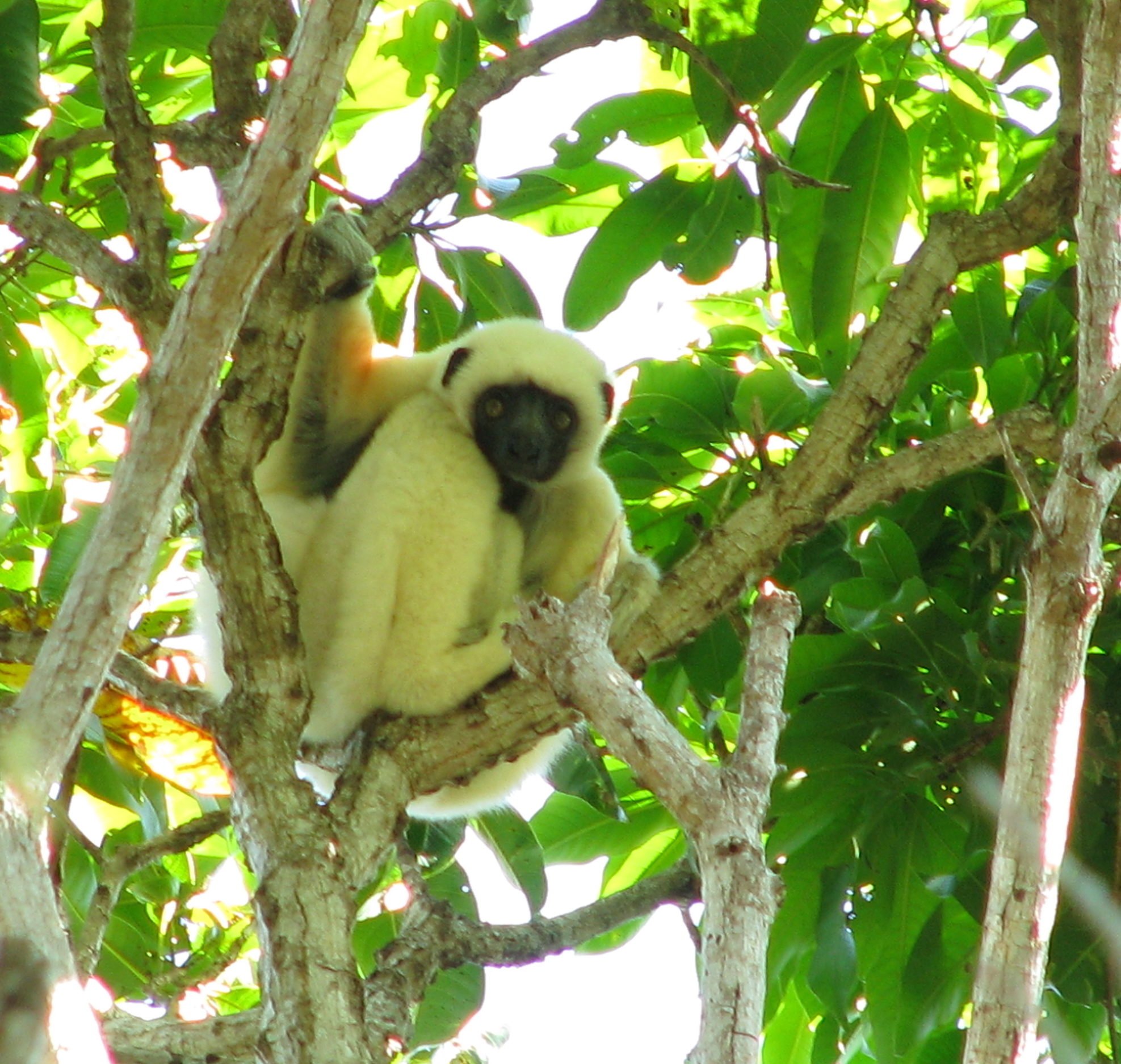
There are 7 species of lemurs including the Propithecus deckenii, 5 species of reptiles and 1 species of amphibians. The avifauna is represented by 112 species with 55 species of water birds.